Oedema Terminology:
Glossary of Useful Wound Care Termsblank
ABPI Assessment
ABPI stands for ankle-brachial pressure index. The ABPI determines the vessel competency of the body by measuring the blood pressure from the ankle and comparing it to that of the arm.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are drugs used to treat bacterial infections. Antibiotics work by destroying or preventing the spread of bacteria.
Atrophie Blanche
Atrophie blanche is scarring caused by a poorly healed ulcer.
Carbon Dressing
Cellulitis
Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common on the lower limbs.
Chronic Oedema
Chronic oedema is the accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues. Oedema is considered chronic if it lasts for more than 3 months. It is usually concentrated in one area of the body (i.e., the ankles).
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency can cause pain, discomfort, oedema, varicose veins, and leg ulcers.
Compression Therapy
The gold standard treatment for oedema is compression therapy. It is also very useful for wound and ulcer prevention.
Debridement
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Dermatitis
Dermis
The dermis is the middle layer of the skin. It is located between the epidermis and hypodermis. The dermis is the thickest layer of the skin and is made of elastic and fibrous tissue.
Diuretics
Doppler Ultrasound
Elevation
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin. It is located above the dermis and the hypodermis.
Exudate
blank
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is the abnormal thickening of the outer layer of skin, known as the stratum corneum. This is the result of an abnormal quantity of keratin-producing cells. It is localised to the legs and feet, which is why it usually affects patients with lymphoedema and chronic venous insufficiency.
Infection
A reaction caused by microorganisms such as bacteria or viruses invading the body.
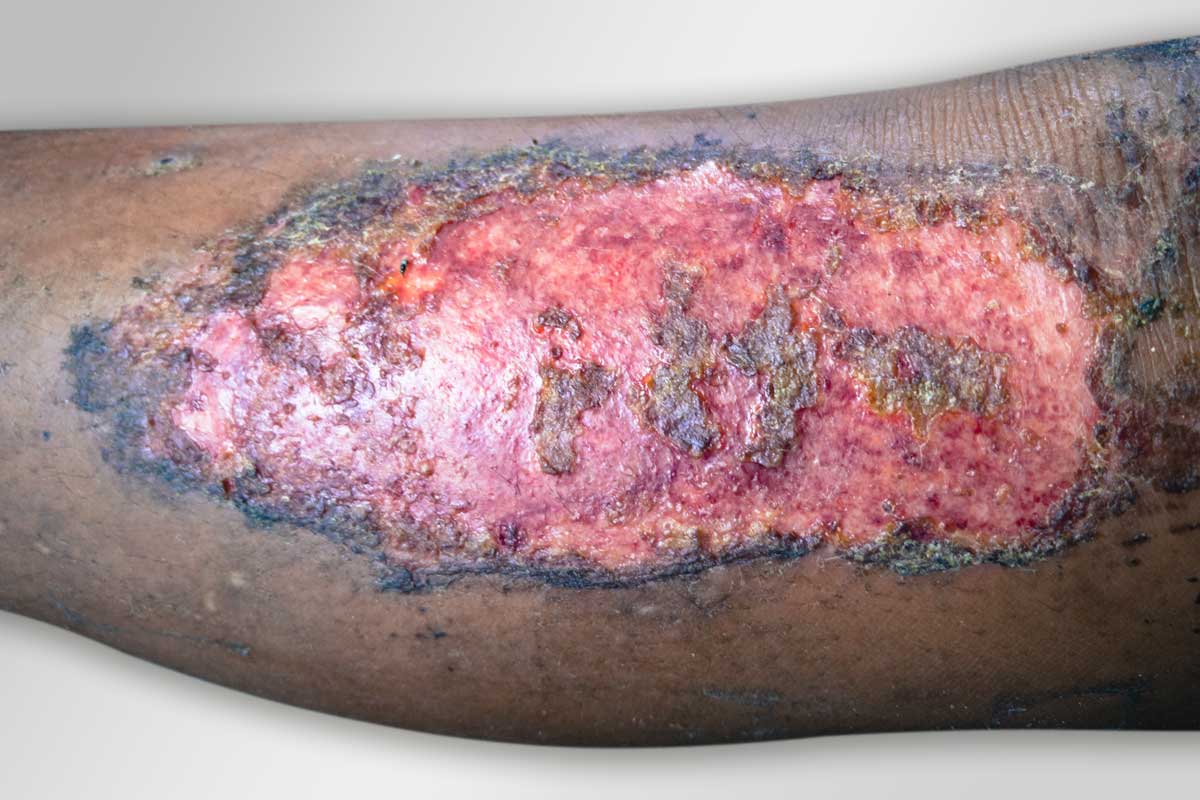
Leg Ulcer
Leg ulcers are wounds in the lower limbs that take more than 4-6 weeks to heal. Leg ulcers can vary in severity from person to person. Leg ulcers are normally caused by comorbidities such as chronic venous insufficiency and arterial disease.
Lipodermatosclerosis
Lipodermatosclerosis is an inflammatory condition that affects the skin on the lower limbs.
Lipoedema
Lipoedema is a chronic condition that involves an abnormal accumulation of fat cells in the legs and buttocks. Lipoedema can affect the arms, but this is rare.
Unlike normal weight gain, lipoedema can feel painful and heavy. It can also bruise easily.
Lipoedema overwhelmingly affects women.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a part of the body’s immune system and plays a crucial role in protecting the body from infection. The lymphatic system is an extensive network of vessels, nodes, and ducts that collect and circulate excess fluid in the body.
The lymphatic system regulates fluid balance, the absorption of fatty acids in the stomach, and the elimination of dangerous cells like bacteria.
Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema occurs when the lymphatic system stops working properly.
Besides the swelling, other symptoms include heaviness, skin infections, folds in the skin, difficulty moving, and leakage of fluid through the skin.
Lymphorrhea
Lymphorrhoea is the leakage of lymph through the skin. In most cases, it results in a large volume of fluid being released from the body, which can soil clothes, bedding, and floors.
Maceration
Maceration is the softening and breaking down of the skin, especially the periwound, because of prolonged exposure to moisture.
Malodour
Malodour is defined as a foul or unpleasant smell. Wound malodour can be a sign of infection or a reaction to certain dressings. Malodour can be problematic for healthcare providers and patients. It can lead to embarrassment, stress, isolation, and nausea.
Periwound
The periwound is defined as the skin immediately surrounding the wound bed.
Pus
Pus is a fluid that leaks out of wounds and cuts. It is made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, nutrients, and enzymes. Pus is sometimes known as exudate (see Exudate).
Slough
Slough is considered the by-product of inflammation. Slough is composed of skin cells, fibrin, protein, and microorganisms. It is typically a yellow or off-white colour. The presence of slough can increase the risk of maceration, infection, and malodour.
Superabsorbent Dressing
Superabsorbent dressings are designed to absorb and retain large volumes of exudate and fluid. Many superabsorbent dressings are developed to keep fluid away from the wound bed to maintain adequate moisture balance.
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are swollen and enlarged veins that typically occur on the legs and feet. They are often blue and purple in colour.
They are usually a sign of venous insufficiency.
Venous Leg Ulcer
Venous leg ulcers are caused by chronic venous insufficiency. They are chronic and slow-healing wounds that develop on the gaiter area of the lower limbs. They are the most common type of leg ulcer, accounting for around 60% of all cases.
Leg Ulcer Education

Leaky Legs Education

Healthy Legs Education
Disclaimer:
Please note that while every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content presented, it is purely for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
