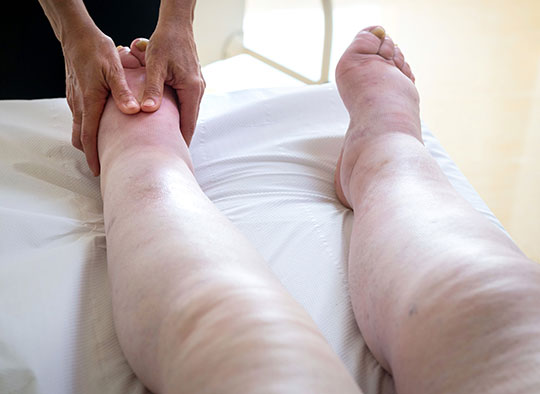
What skin changes are associated with chronic oedema?
Chronic oedema is defined as the atypical swelling of the lower limbs caused by an increase in fluid in the tissue that lasts more than three months.[1]
Chronic oedema can have several physical and emotional implications that affect a patient’s quality of life, including discomfort, leaking, ulceration, embarrassment, and social isolation.
It is critical to remember that chronic oedema is primarily the symptom of an underlying condition. As a result, the key to managing the oedema is locating and addressing its primary cause.
The importance of the skin is often overlooked when thinking about chronic oedema. Changes in the skin, however, can be some of the primary indicators of two of the most common conditions affecting the lower limbs: chronic venous insufficiency and lymphoedema.[2]
Although these conditions share some characteristics, namely oedema, there are some notable skin features that are unique to each of them. These skin features, together with a medical assessment and routine tests, can be used to diagnose the underlying condition that is responsible for the oedema.
What skin changes are associated with CVI and lymphatic disease?
• Varicose veins – swollen and enlarged veins around the legs and feet.
• Atrophie blanche – scarring caused by a poorly healed ulcer.
• Lipodermatosclerosis – inflammatory condition that affects the skin on the lower legs.
• Hyperkeratosis – a build-up of keratin that causes the thickening of the skin’s outer layers.
• Dermatitis – a general term for skin irritation, including dryness, itchiness and flaking.
• Venous leg ulcer – a chronic and slow healing wound caused by CVI.
• Lymphorrhoea – lymph fluid leaking from the surface of the skin.
• Papillomatosis – wart-like tumours growing in the respiratory tract.
• Hyperkeratosis – a build-up of keratin that causes the thickening of the skin’s outer layers.
• Lymphadenopathy – swollen lymph nodes.
References:
- Bianchi, J et al. Chronic Oedema Made Easy. Wounds UK 2012; 8(2): 1
- Ibid:1
Resources:
Product website:
Other related articles:
Disclaimer:
Please note that while every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content presented, it is purely for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.